Weebit Nano licenses its RRAM technology to onsemi
RRAM developer Weebit Nano announced that it has licensed its RRAM memory technology to onsemi, a tier-1 semiconductor supplier.
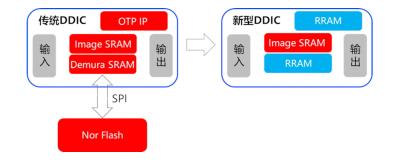
Under the terms of the agreement, Weebit ReRAM IP will be integrated into onsemi’s Treo platform, to provide embedded non-volatile memory (NVM). Weebit ReRAM integration into a Bipolar CMOS, DMOS (BCD) process provides a low-power, cost-effective NVM that has proven excellent retention at high temperatures.